What is a self charging battery? How can a battery charges itself without external power source? Who has invented this technology? How will it help the Future? Let’s find out.

Table of Contents
Dream Battery:
Do You ever dream of a battery that charges itself and never needs any charging point and charging stations which means no stop for Your car and no cost for charging and electrifying Your home. It means no cutting of trees and burning of coals and building of dams for electricity and infinite of possibilities. If Magic is Science or vice versa , the magical battery is on it’s way to be developed in Australia in the years to come. But now soon in months, though in a small scale, the technology can power Your fitness band that might never need any external power ever.

Strategic Elements, Australia:
An Australian company, Strategic Elements , which has a listing in the Australian Stock Exchange, has claimed of working on a Self Charging Battery that can create electricity from humidity in the air or skin surface. If developed, these batteries will be literally everlasting. According to the company ” This technology targets the global multi-billion dollar battery market for IOT devices. It has the potential to enable batteries to self-charge from the humidity in the air, potentially removing the need for manual charging or wired powered.” The share of the company rose to more than 40 percent on the Stock Exchange of Australia after Strategic Elements announced about the project. Strategic Elements has named the technology as ” Energy Ink”
The Collaboration:
Strategic Elements has collaborated with the University of New South Wales and the CSIRO ( Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organization) to work and develop this self powered battery. The company claims that their technology already makes more than enough energy that runs ” most existing devices in the large US 10 billion dollar Electronic Skin Patch market”. As human body already produces a lot of moisture , the self charging battery included device just only needs to be put on human skin to make it run for years and decades.
The University of New South Wales has a great experience in electronic inks, energy harvesting and storage over 10 years and it is applied to the ‘Energy Ink ‘ technology.
The Technology:
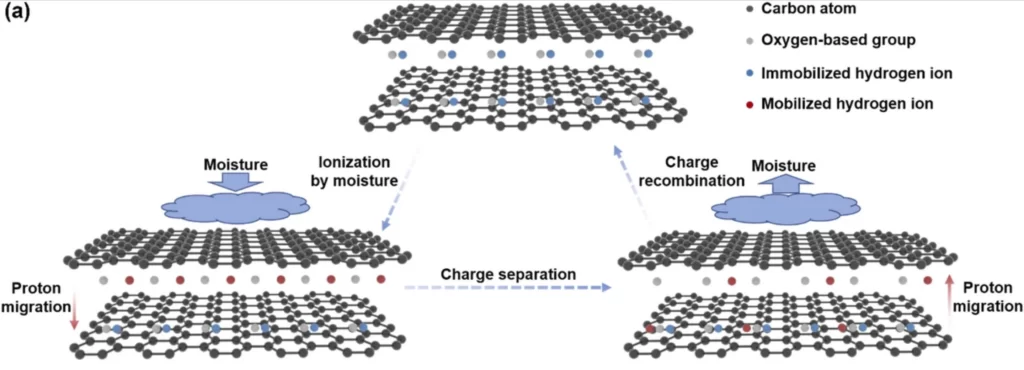
According to Strategic Elements website ” The battery technology is a liquid ink based on graphene oxide that is able to harvest energy from the humidity in the air or skin surface to self-charge themselves within minutes “. The Graphene oxide coating is fabricated onto glass and connected with battery cells to charge it through moisture. Multiple batter cells are connected to harvest larger amount of current. Even the technology is aiming to get more current at less humid air.
The aim of using sustainable, green and safe materials have been maintained that are suitable for human skin contact.
The Sucess:

The team has been able to produce 3.7 volt of current in connected cell prototypes. The recharge time of a battery has been achieved to more or less 3 minutes. About 36 square centimetre battery cells that are suitable for electronic skin patches are produced. Further work to increase the EnergyInk cell size area to 100 square centimetres is going on.
As Graphene based materials are able to produce energy from moisture and heat, the magic of the technology lies in it’s simplicity to understand the Nanoionic characteristics of materials and the effort to find alternative solution to everyday need of constant energy for running a modern life smoothly. The IoT ( Internet of Things) devices, which the technology is aiming to power is going to be a very important and necessary building blocks of tomorrow’s life. Without compromising with nature and minimally exploiting Natural Stability, the production of Energy is possible and We have to find more new ways to make it happen.
The Future :

Strategic Elements stated “ it wasn’t long ago that many said it was impossible to produce any usable energy from moisture. Our team experienced a lot of scepticism. For us to now realistically target the ampere hour range generation of electrical energy solely from humidity in the air is a huge achievement. Our Technology doesn’t relies on rare materials and carries no safety risks and in addition can provide flexibility to electronics.”
The potential to increase the electrical charge capacity from miliamp-hours ( mAh) to ampere-hours (Ah) establishes the hope that We have on the technology in future.
This technology, though seems to be at a small scale at now might open a new era of discovery of green energy solutions in future. The tropical countries, mainly have no dearth of moisture readily available in the air and just like solar cells, moisture cells might be developed to produce energy without harming the environment a bit.
(IF YOU LIKE THIS , PLEASE SHARE THIS ARTICLE TO YOUR FRIENDS AND FAMILY TO CREATE AWARENESS OF SUSTAINABILITY)

FAQ:
What is a self- charging battery?
A self charging battery is a battery cell or group of cells that need to external power source to recharge it, rather it can recharge on it’s own.
From Where it gets Power?
The Self Charging Battery gets Power from the charging cells that produces power from humidity of the air and human skin just like batteries powered from Solar energy by solar cells.
How powerful the battery is? Can it run an EV? Why are We excited that much?
At present, the battery can run Your wristband and fitness devices that we wear. It is not very big to power an EV.
But who knows, this technology in the future might develop and grow into a device that can power EVs or even homes. Nobody can predict, that will not happen. Every technological growth has a humble beginning. Imagine the first computers or the hard drives.
Is the battery available at the market now?
No, not yet. By September,2022 the final results are expected.
(Featured image courtesy: deposit photos. Courtesy: newatlas.com and proactiveinvestors.com. Images used are never intended for copyright violation.We acknowledge sincere gratitude to all the image owners)
